 2022-11-23
2022-11-23
 2023-09-04
2023-09-04The consumption of graphite electrodes is mainly related to the quality of the electrodes themselves, as well as to steelmaking operations and processes.(1) Electrode end consumption. Its consumption includes the sublimation of graphite material caused by high arc temperature, as well as the loss of chemical reactions between the electrode end and molten steel and slag. The electrode end consumption is also related to whether the electrode is inserted into the molten steel to increase.(2) Oxidation loss on the outer surface of the electrode. In recent years, in order to improve the smelting rate of electric furnaces, oxygen blowing has been widely used, which has led to an increase in electrode oxidation losses. In general, the oxidation loss on the outer circular surface of the electrode accounts for about 50% of the total electrode consumption.(3) Residual loss of electrodes or connectors. A small section of electrode or connector that is continuously used at the connection between
 2023-08-29
2023-08-29(1) Carbon based materials: Most carbon based materials use asphalt, but in order to control the filling rate, tar or asphalt is often mixed with low carbonization rate and low viscosity carbon based materials such as tar and creosote. They are carbonized through heat treatment after impregnation, so the residual material entering the pores is only carbon. The carbon process is currently a standard carbon process aimed at improving density, strength, conductivity, thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and wear resistance. It has become the most common treatment method for general carbon materials, especially in the production process of fine structured graphite and UHP electrodes for electric furnace steelmaking. It is an indispensable process. In order to achieve the same goal, there are also cases of impregnating synthetic resin and then roasting and carbonization. The carbonization of synthetic resin generally generates hard carbon, which is characterized by greatly increasin
 2023-08-29
2023-08-29(1) Small specification graphite electrodes and joint blanks, various specifications of graphite anodes, fine structure, high-strength, and high-density graphite. These products need to have high density and strength, as well as low electrical resistivity, so the baked semi-finished products are first impregnated with coal tar pitch and then graphitized.(2) Diaphragm type salt solution electrolysis cell graphite anode. Graphite anodes impregnated with coal tar pitch can generally last for 8-9 months, while graphite anodes that are not impregnated can only last for 5-6 months. The main reason for affecting the lifespan of graphite anodes is that the electrolyte penetrates into the pores of the anode, while hydroxide ions, sulfate ions, and hypochlorite ions in the electrolyte discharge on the anode, generating primary oxygen. This initial oxidation reaction of oxygen on the anode causes chemical corrosion, which accounts for about half of the loss. Additionally, chemical corrosion weak
 2023-08-29
2023-08-29(1) Select the appropriate electrode variety and diameter based on the capacity of the electric furnace and the equipped transformer capacity.(2) During the loading, unloading, and storage of graphite electrodes, attention should be paid to preventing damage and moisture. The electrodes that are affected by moisture should be dried by the electric furnace before use. When lifting, the joint holes and surface threads of the electrodes should be protected.(3) When connecting the electrode, compressed air should be used to blow off the dust in the connector hole. The force used to screw the connector into the electrode connector hole should be stable and uniform, and the tightening torque should comply with regulations. When holding the electrode, it is necessary to avoid the joint area, that is, clamp it above or below the bottom of the electrode joint hole.(4) When loading furnace materials into the electric furnace, in order to reduce the impact of furnace material collapse on the ele
 2023-08-28
2023-08-28The factors that affect the impregnation effect include: firstly, the impregnation process conditions (such as temperature and pressure), and secondly, the physicochemical properties of the impregnation.Influence of process conditions(1) Temperature (product preheating temperature, impregnation tank temperature, impregnation agent temperature), depending on the impregnation process: 1. The product is preheated too high and is prone to oxidation; The temperature is too low, and when it comes out of the preheating box, it quickly cools down and enters the impregnation tank. When the impregnating agent encounters cold products, its viscosity increases and its fluidity deteriorates, resulting in poor impregnation effect. 2. If the tank temperature is too high, asphalt is prone to oxidation condensation reaction, viscosity will also increase, and flowability will deteriorate; The tank temperature is too low, the fluidity of asphalt is also poor, and the impregnation effect is not ideal.(2)
 2023-08-28
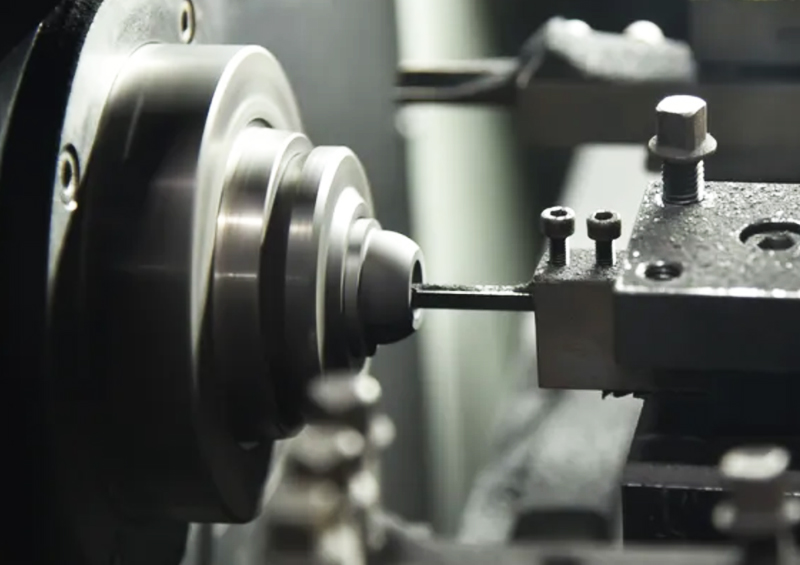
2023-08-28Various carbon graphite products, although they have a certain shape and size after forming, undergo expansion and contraction, deformation and bending, collision or corner dropping during the process of roasting, impregnation, and graphitization treatment from the pressed blank to the graphitized blank. The surface adheres to some fillers and insulation materials, resulting in roughness and unevenness. Their shape and size change to a certain extent, and they cannot achieve the shape of the product during use, Due to strict requirements for size and surface roughness, it cannot be used without mechanical processing. In addition, some products have complex structures and shapes that cannot be directly produced by forming methods, such as metal continuous casting and rolling graphite crystallizers, electric spark machining graphite molds, carbide sintering graphite boats, discs, and other special graphite products. Some products require interconnection when used, such as the connection