 2022-11-23
2022-11-23
 2023-10-27
2023-10-27The graphite crucible must be strictly protected from moisture and must be stored in a dry place or on a wooden frame. When handling graphite crucibles, it is important to handle them with care and prevent them from falling or shaking. Before using them, they should be baked in a drying equipment or by the furnace to raise the temperature to 500 ℃. The graphite crucible should be placed below the surface of the furnace mouth to prevent wear and tear on the furnace cover. When adding materials, it should be based on the solubility of the crucible, and too much material should not be added to prevent tightening the crucible. The furnace outlet and crucible clamp should conform to the shape of the crucible, and the clamp in the middle should prevent damage to the crucible due to stress on the department. When removing slag and coke from the inner and outer walls of the crucible, it should be gently knocked to prevent damage to the crucible. A suitable distance should be maintained betwee
 2023-10-27
2023-10-27Graphite crucibles have good thermal conductivity and high temperature resistance. During high-temperature use, their coefficient of thermal expansion is small, and they have certain strain resistance for rapid heating and cooling. Strong corrosion resistance to acid and alkaline solutions, with excellent chemical stability. Graphite crucibles, due to their excellent performance, are widely used in industries such as metallurgy, casting, machinery, and chemical engineering for the smelting of alloy tool steel and the melting of non-ferrous metals and their alloys. And it has good technical and economic effects. The production of domestic graphite crucibles has reached or even exceeded that of imported crucibles:1. The high density of graphite crucibles enables them to have good thermal conductivity;2. The graphite crucible has a specially made and dense molding material on its surface, greatly improving the corrosion resistance of the product and extending its service life;3. The ther
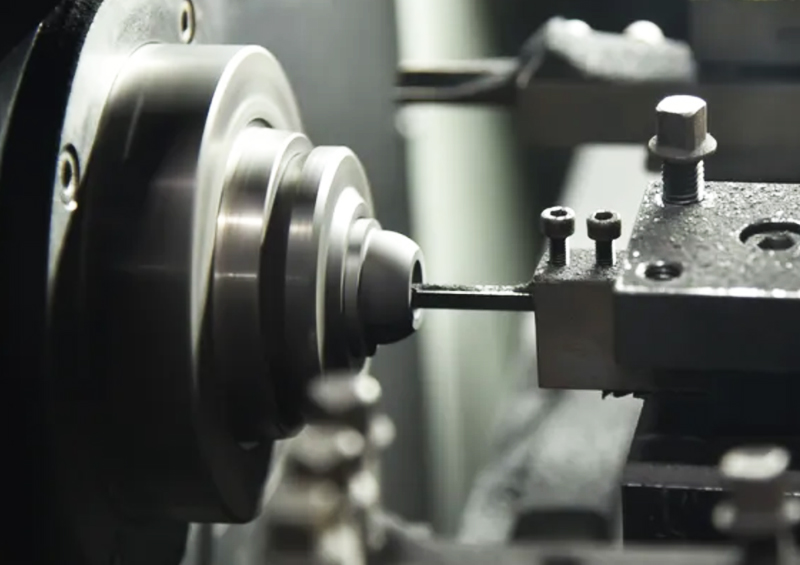
 2023-10-26
2023-10-261、 Fast speed;Graphite discharge is 2-3 times faster than copper, and the material is not easily deformed. It has obvious advantages in the processing of thin ribbed electrodes. Copper has a softening point of around 1000 degrees, which is prone to deformation due to heating. The sublimation temperature of graphite is around 3650 degrees, and compared to copper, the thermal expansion coefficient of graphite material is only 1/30 of that of copper material;2、 Lightweight;The density of graphite is only 1/5 of that of copper. When using large electrodes for discharge machining, it can effectively reduce the burden on machine tools (EDM) and is more suitable for the application of large molds;3、 Low loss;Due to the presence of C atoms in spark oil, during discharge machining, high temperatures cause the C atoms in spark oil to decompose, forming a protective film on the surface of the graphite electrode, compensating for the loss of the graphite electrode;4、 No burrs;After the copper ele
 2023-10-26
2023-10-26Graphite crucibles have a wide range of uses in the metallurgical industry, and their main function is to hold various liquid metals. As a metallurgical manufacturer, it is necessary to use graphite crucibles, otherwise there may be some problems in later production and use.Although graphite crucibles are of good quality and not easily damaged, they should also be handled with care. Falling or bumping from high altitude may not have a significant impact on its quality, but if it continues to do so for a long time, it may crack or even break. After this situation occurs, there is no way to remedy it, and we can only replace it with a new one.2. Graphite crucibles are prone to moisture, and the product will become soft after being affected by moisture. When struck by some impactful objects, it will deform. And once water enters the graphite crucible, it will affect the raw materials contained inside, causing dilution of the raw materials, and even causing some chemical reactions to furt
 2023-10-25
2023-10-25Carbon products can be divided into graphite electrode, carbon block, graphite anode, carbon electrode, paste, electrochar, carbon fiber, special graphite, graphite heat exchanger, etc. according to their usage. Graphite electrodes can be classified into ordinary power graphite electrodes based on the allowable current density. High power electrode, ultra high power electrode. Carbon blocks can be divided into blast furnace carbon blocks, aluminum carbon blocks, electric furnace blocks, etc. according to their purpose. Carbon products can be divided into carbon products, graphite products, carbon fibers, and graphite fibers according to the processing depth. Carbon products can be divided into graphite products, carbon products, carbon fibers, special graphite products, etc. according to different raw materials and production processes. Carbon products can be divided into multi ash products and low ash products (with ash content less than 1%) based on their ash content.The national an
 2023-10-25
2023-10-25(1) Graphite electrodes are mainly made from petroleum coke and needle coke as raw materials, and coal tar pitch as a binder. They are made by calcination, batching, kneading, pressing, roasting, graphitization, and machining. They are conductors that release electrical energy in the form of an arc in an electric arc furnace to heat and melt the furnace material. According to their quality indicators, they can be divided into ordinary power, high power, and ultra-high power. Graphite electrodes include:(1) Ordinary power graphite electrode. Allowing the use of graphite electrodes with a current density below 17A/cm2, mainly used for ordinary power electric furnaces such as steelmaking, silicon smelting, and yellow phosphorus smelting.(2) Anti oxidation coated graphite electrode. A graphite electrode coated with an antioxidant protective layer on the surface forms a protective layer that is both conductive and resistant to high-temperature oxidation, reducing electrode consumption duri